Hepatitis B
Definition
The term "hepatitis" refers to syndromes or diseases causing liver inflammation, including inflammation due to viruses and chronic alcohol abuse. Viruses causing hepatitis include Hepatitis A, B, C, E, and the delta factor. Each virus causes a distinct syndrome, though they share some symptoms and consequences.
Most people who become infected with hepatitis B get rid of the virus within 6 months. A short infection is known as an "acute" case of hepatitis B.
Causes
Hepatitis B is transmitted via blood and other body fluids. Infection can occur through:
- Contact with blood in healthcare settings -- this puts physicians, nurses, dentists, and other healthcare personnel at risk
- Unsafe sex with an infected person
- Blood transfusions
- Sharing needles during drug use
- Receiving a tattoo or acupuncture with contaminated instruments
- Birth -- an infected mother can transmit the virus to the baby during delivery or shortly thereafter
People who are at higher risk, including healthcare workers and those who live with someone with hepatitis B, should get the hepatitis B vaccine.
In acute hepatitis, it takes about 1-6 months from the time of infection until symptoms appear. Early symptoms may include nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, fatigue, and muscle and joint aches. Jaundice, together with dark urine and light stools, follows. About 1% of patients infected with hepatitis B die due to liver damage in this early stage.
The risk of becoming chronically infected depends on the person's age at the time of infection. More than 90% of newborns, about 50% of children, and less than 5% of adults infected with hepatitis B develop chronic hepatitis.
Most damage from hepatitis B virus is caused by the body's response to the infection. The body's immune response against the infected liver cells (hepatocytes) damages the cells, causing liver inflammation (hepatitis). As a result, liver enzymes (transaminases) leak out of the liver into the blood, causing transaminase blood levels to be elevated. The virus impairs the liver's ability to produce the clotting factor prothrombin, increasing the time required for blood clot formation (prothrombin time).
Liver damage also impairs the body's ability to rid itself of bilirubin (a breakdown product of old red blood cells), causing jaundice (yellow discoloration of the eyes and body) and dark urine.
Symptoms
- Fatigue, malaise, joint aches, and low-grade fever
- Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and abdominal pain
- Jaundice and dark urine due to increased bilirubin
Exams and Tests
- Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) -- this represents the first viral marker present in blood tests after the patient is infected. It usually disappears from the blood in 1-2 months.
- Hepatitis B core antibody (Anti-HBc) -- this is usually detected within 1-2 weeks of the appearance of hepatitis B surface antigen.
- Hepatitis B surface antibody (Anti-HBs) -- this is found both in those who have been immunized and those who have recovered from hepatitis infection.
- Both hepatitis B surface antibody and core antibody persist indefinitely in the blood of patients who have recovered from hepatitis B.
- Liver enzyme (transaminase) blood levels may be elevated due to liver damage.
- Albumin levels may be low and prothrombin time may be prolonged due to severe liver failure.
Illustrations and Images
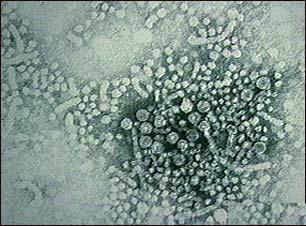
Hepatitis B
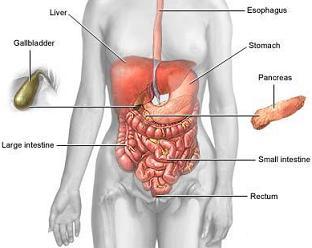
Digestive System
Source: Portal Content Team
Related resources
ફેરફાર કરાયાની છેલ્લી તારીખ : 2/12/2020
This topic covers information about Amoebic Liver ...
Acne causes, symptoms and remedies are described h...
This topic deals with information related to Anima...
Reasons for discharge from ear, symptoms and preca...
